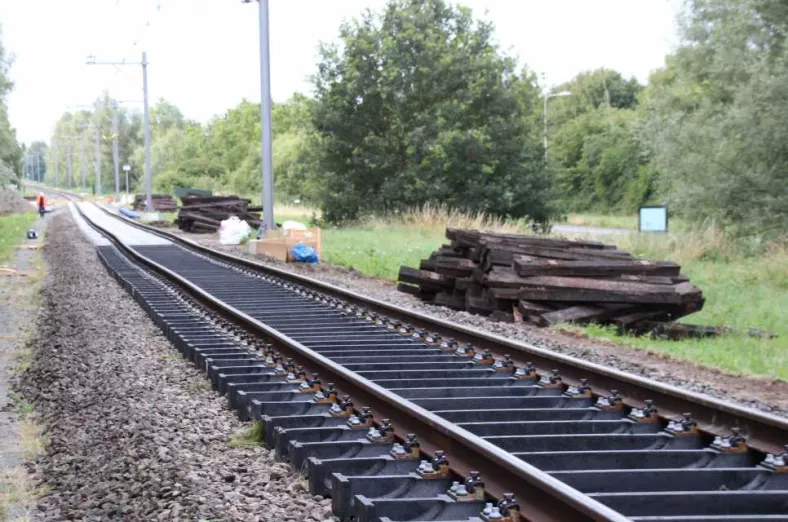
Smart railway sleepers with multi-sensor solution


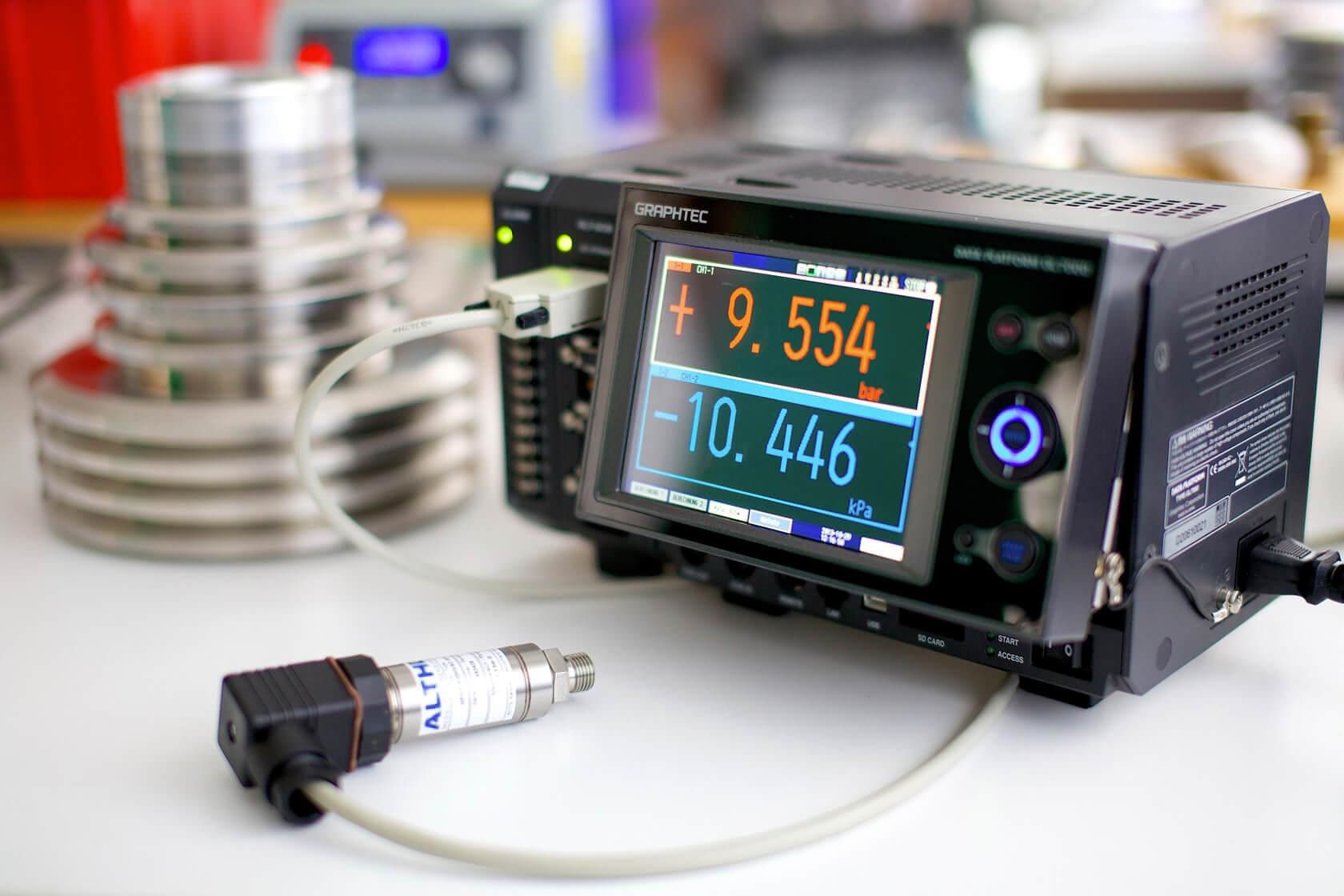
High-quality measuring devices for measuring temperature, pressure, humidity, voltage and the automation of industrial processes: Efficient and reliable.

We offer our customers amplifiers, solutions for measurement data acquisition and measurement solutions for all individual requirements. Load cells, modules and systems are specially customised to your applications. With our comprehensive hardware and software solutions, including bus-compatible evaluation electronics, you can successfully and effectively automate your industrial weighing processes (OIML).
Whether you are filling juice or dosing the correct amount of an ingredient for a medicine, you can automate your processes with the weighing solutions from our extensive range. Your machines work independently, even more precisely and achieve optimum results. Our standard or customised measurement data acquisition systems are used for complex industrial control systems in many different industries.
Measuring instruments are technical devices that can measure, monitor and visualise physical, chemical or electrical quantities. They are indispensable for precisely recording data and optimising processes in science, industry, medicine, technology and everyday life. Measuring devices provide precise measured values, often with a defined measurement uncertainty. Most measuring devices can and must be calibrated regularly to ensure that the results remain correct. The most important areas of application include industry and manufacturing, research and development as well as medicine and health.
Electrical measuring devices measure electrical quantities such as current, voltage, resistance, power, capacitance, inductance, etc. These devices include, for example, multimeters for measuring current, voltage and resistance as well as oscilloscopes (showing voltage curves over time), resistance meters and data loggers for electrical quantities that record voltage, current and energy consumption over a longer period of time. Electrical measuring devices often use measuring amplifiers to amplify weak signals. Examples include differential amplifiers for precise voltage measurement. They are often used in electronics, electrical engineering and energy technology to analyse and monitor electrical systems.
These devices measure physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, mass, length, time, speed, force, energy, etc. These include thermometers, barometers, scales, force gauges and data loggers. Physical measuring amplifiers amplify signals from strain gauges, force sensors or acceleration sensors. They are used in physics, engineering, meteorology and many other areas in which physical properties need to be analysed.
Both types of measuring devices are used to obtain precise data and to monitor and analyse processes or phenomena. Electrical measuring devices measure quantities within the electrical system, while physical measuring devices focus on physical properties outside the electrical context. Electrical measuring devices often require a power source, while physical measuring devices are often mechanical in nature. In practice, the categories often overlap, as physical quantities (e.g. temperature, pressure) can also be measured using electrical signals, for example by using sensors, data loggers and measuring amplifiers.
Tailor-made or complete customized. We are happy to help you!
Data loggers are electronic devices that record physical or chemical measured variables (such as temperature, humidity, pressure, light, voltage, current, etc.) continuously or at specific intervals, store them and make them available for later analysis. They consist of sensors, a memory unit and often a software interface for analysing the data.
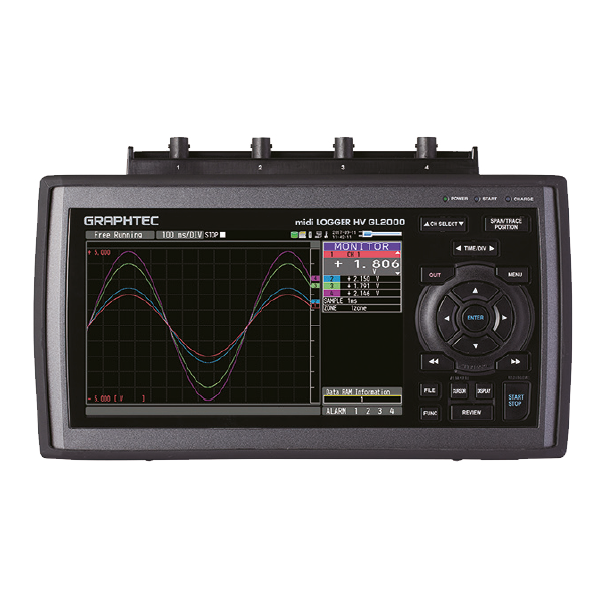
Data loggers record physical or chemical variables using special sensors, store the recorded values and enable them to be analysed later. The sensors measure the desired parameters, such as temperature, humidity or pressure, continuously or at specific time intervals. The collected data is saved in the device's internal memory or on external storage media such as an SD card. Many data loggers also have a real-time clock to precisely time the measurement results. The stored information can then be transferred to an end device via various interfaces - such as USB, WLAN or Bluetooth - and analysed and visualised using special software. This makes it possible, for example, to recognise trends, create diagrams and document reports.



Measuring amplifiers are electronic components or devices that amplify weak electrical signals from sensors or measuring transducers in order to make them usable for further processing, display or storage. These amplifiers play a central role in measuring systems, as the signals from sensors are often very small and susceptible to interference. A measuring amplifier ensures that these signals are reliably recorded and converted into an amplified, low-interference form.
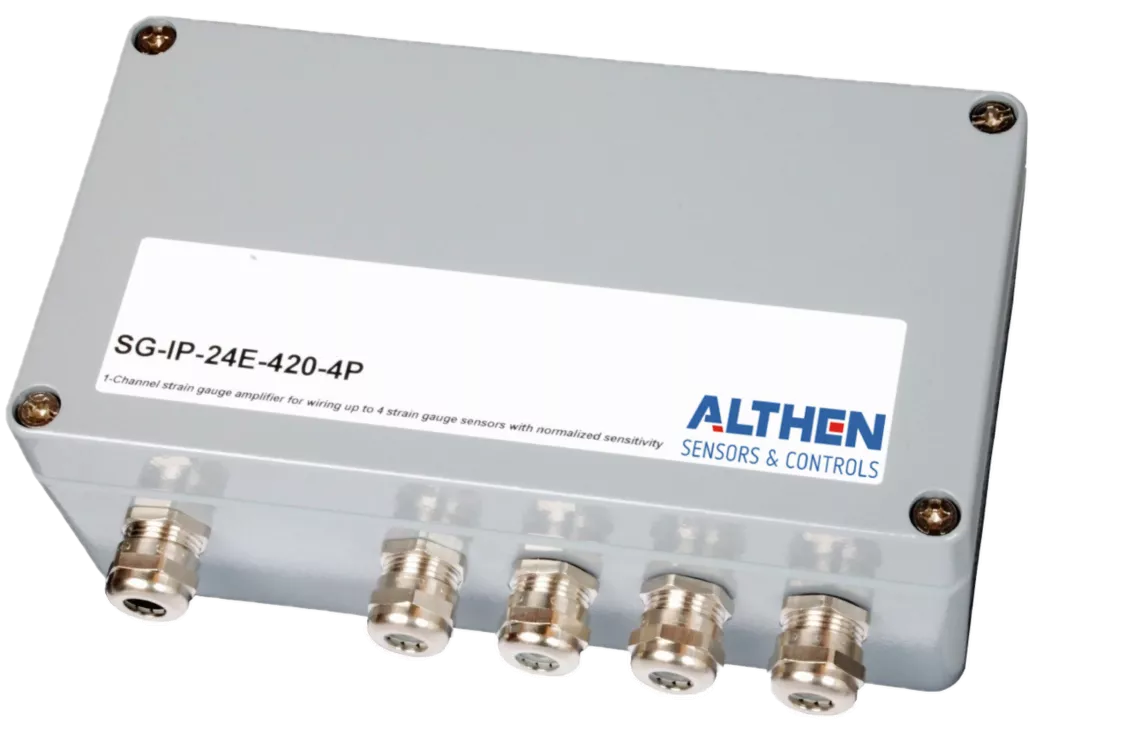

Measuring amplifiers take the weak output signals from a sensor or transducer, amplify them proportionally and prepare them for downstream devices or systems. They usually consist of precise operational amplifiers and electronic filters that amplify the signal and reduce interference signals (such as noise or interference). A differential amplifier is often used, which amplifies the difference between two inputs and eliminates interfering DC voltage components. The output of the measuring amplifier then provides an amplified signal that is passed on to a display, a data acquisition system or a control system, for example.
An important part of the function is the adaptation to different sensors and measuring ranges. Measuring amplifiers therefore often offer setting options to adjust amplification factors (gain) or offset corrections and to optimally amplify the signal.
Measuring amplifiers are used in numerous applications and industries, especially where small signals need to be precisely recorded and processed..

Althen Sensors & Controls is certified to ISO 9001. It is the most widely used and most important standard in quality management. ISO 9001 focuses on the optimisation of processes in order to improve performance within the company and meet customer requirements in the best possible way. This certification confirms that we reliably fulfil the high quality requirements of our stakeholders and ensure the continuous improvement of our business processes.




Tailor-made or complete customized. We are happy to help you!