During the project WLPI Sensors were used to monitor the change in the condition of the harbour. The optical sensors were compared with normal electrical sensors. The municipality of Rotterdam was very interested in this type of sensors, especially because of its unique properties and the fact that they can be used in an EX zone without problems.
The government was asked to be able to measure real-time during the placement of the tubes to see what is happening at the bottom of the channel. The reason for this, was the fact that there was a pipeline for drinking water and cables for electricity and internet / telephone at the bottom of the channel, only a few meters from where the tubes would be placed. By monitoring during the process, the operator was able to stop when the bottom of the channel would drop significantly.
Installing the Sensors
The sensors were installed in a plastic tube was placed on the bottom of the channel by professional divers. Together with the optical sensors, traditional sensors were also installed in the same tube for reference values based on the existing conventional pressure-sensitive technology. With fiber optical, hydrostatic pressure sensors the movements of the bottom of the channel have been made visible.

Identical measurements
During the installation of the two large tubes, the measurement results happily only see a little movement in the soil, so that the placement of the piles was successfully completed. After analysing the added value of both the traditional sensors and the optical fiber sensors, it could be concluded that the measurements were identical.Therefore, it could be said that the pilot was successfully implemented so that more projects could benefit in the future from the unique properties of these glass fiber sensors.
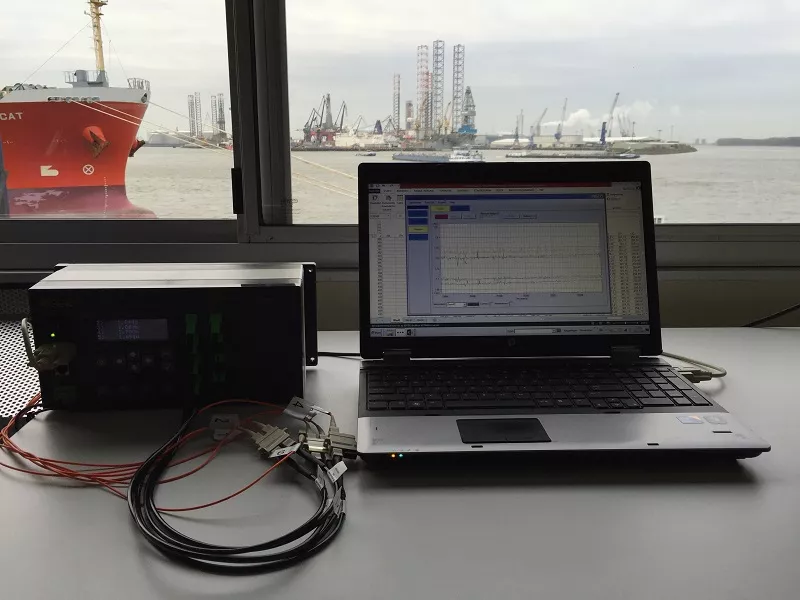
Remote monitoring
One of the great advantages offered by the fiber optic solution was the possibility to set up the final distribution at about 500 meters from the location where the work was being done. The instrumentation could thus be placed in the temporary offices for remote monitoring. Because the fiber optic cable is intrinsically safe, there was no problem to lead the cable on shore through an EX zone.
A much more complicated system therefore had to be rolled out for the electrical sensors. traditional sensors were also installed in the same tube for reference values based on the existing conventional pressure-sensitive technology.
Conclusion of the pilot project
Optical Sensors based on fiber optics already have many advantages over electrical sensors, but with the new WLPI technology there are still a number of advantages. Especially when it is used for large distances between sensor and measuring station or if there is an EX situation, this technology is very interesting.
Products

OPP-C Fiber Optic Pressure Sensors
- Measurement range 1.72 to 103 bar
- Maintenance free
- Intrinsically safe

OPP-B Fiber Optic Pressure Sensors
- Measurement range 1.72 to 70 bar
- No drift over time, reliable results during years
- Intrinsically safe
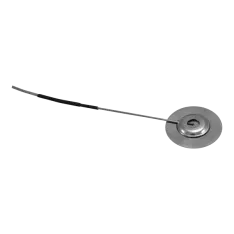
OPP-GF Fiber Optic Pressure Sensors
- Measurement range 1.72 to 3.44 bar
- Small and low weight spot-weldable
- Rugged stainless steel body

